ASM Microbe ‘17 workshop
Room 365
Instructors
- Morten Sommer
- Lejla Imamovic
- Eric van der Helm
- Mostafa Ellabaan
Timetable
- 12:30 Morten Sommer: Introduction to antibiotic resistome
- 12:45 Lejla Imamovic: Resistome profiling (from the lab to databases, overview of the data and analysis to be used during the workshop)
- 13:00 Mostafa Ellabaan: Code examples part 1
- 13:30 break
- 13:45 Code examples part 2
- 14:45 break
- 15:30 Eric van der Helm: Rapid resistome profiling using Nanopore sequencing
- 15:45 Morten Sommer: Antibiotic resistance gene exchange networks
Tasks
-
Task 1. Introduce basic command line and tools how to get the data on/off server Output 1: Ability to use basic commands needed for the workshop (data, database locations etc)
- Task 2. Assign ORFs in GeneMark for selected dataset ((MinION last run) Output 2: Protein (pro) and nucleotide (nt) sequences in fasta format Question: How many ORFs are predicted?
- Task 3. Format databases (e.g. CARD nt and pro or Resfinder nucletide)
Output 3: Database for further use, knowledge on importance of databases
Also mention that one can curate their own database
Task 4A. Annotate insert nt sequences with Resfinder online server (promote DTU) -
Task 4B. Annotate ORFs nt sequences against Resfinder database (blastn) Output 4: Manually curated horizontally transferred list of genes from inserts/contigs and ORFs. Questions: How many inserts have antibiotic resistance gene? Is there a difference between DTU web server (contig) (4A) and annotated ORFs (4B)? - Task 5. Annotate protein sequences against CARD protein database Output 5: List of antibiotic resistance genes from ORFs. Questions: How many inserts have antibiotic resistance gene? Input from participant of interesting hits?
- Task 6. Annotate protein sequences using hmm model in Pfam
Output 6: List of genes from ORFs.
Questions: What can we see from Pfam domain list?
If there is time left, annotate ORFs against optimal databases using plasmid database (to look for mobility).
We can use megablast to map the nt ORFs to plasmid database.
Content
- 1. Login on amazon cloud
- 2. Prepare your directories
- 3. Finding Open Reading Frames (ORFs)
- 4. Install BLAST and HMMer
- 5. The first database, Resfinder
- 6. CARD
- 7. Protein domains using PFAM
Workshop
1. Login in to the Amazon cloud
For Windows users you need to install PuTTy.
You can download it from this website https://www.chiark.greenend.org.uk/~sgtatham/putty/latest.html. install this “putty-64bit-0.69-installer.msi” on your machine.
Run PuTTy on your computer
You will see a screen like this
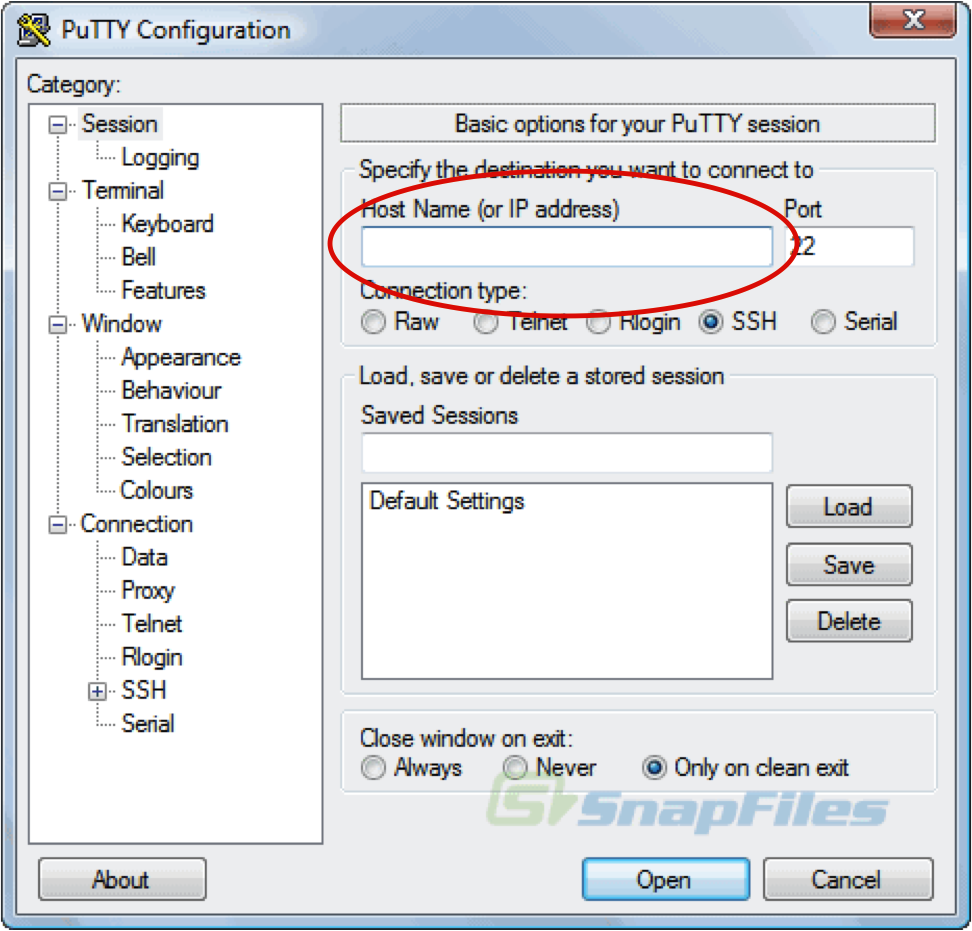
Session:
Host Name: 34.207.202.240
A pop-up will appear like this, click on Yes
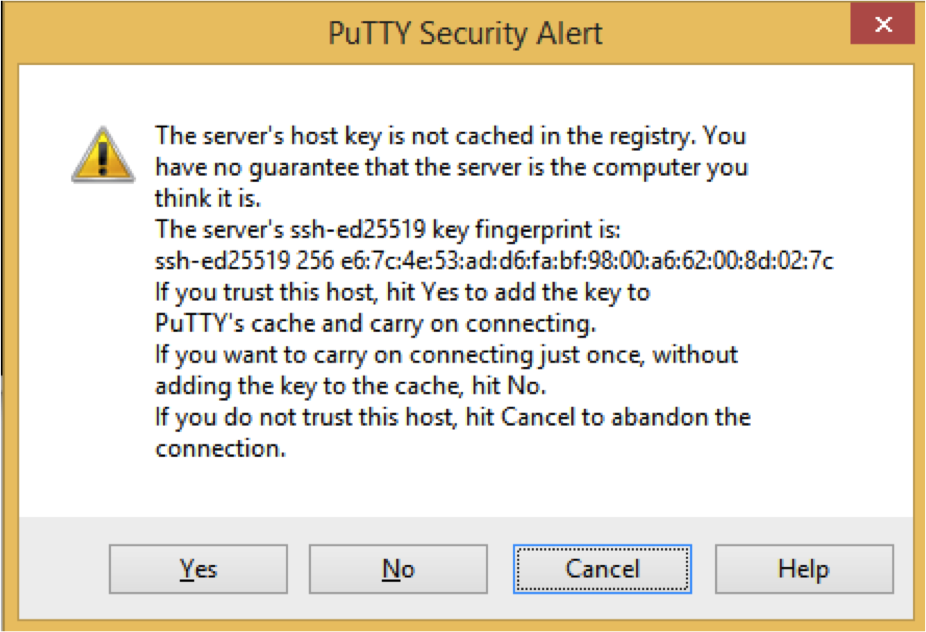
Fill in the username-that-will-be-handed-out and password
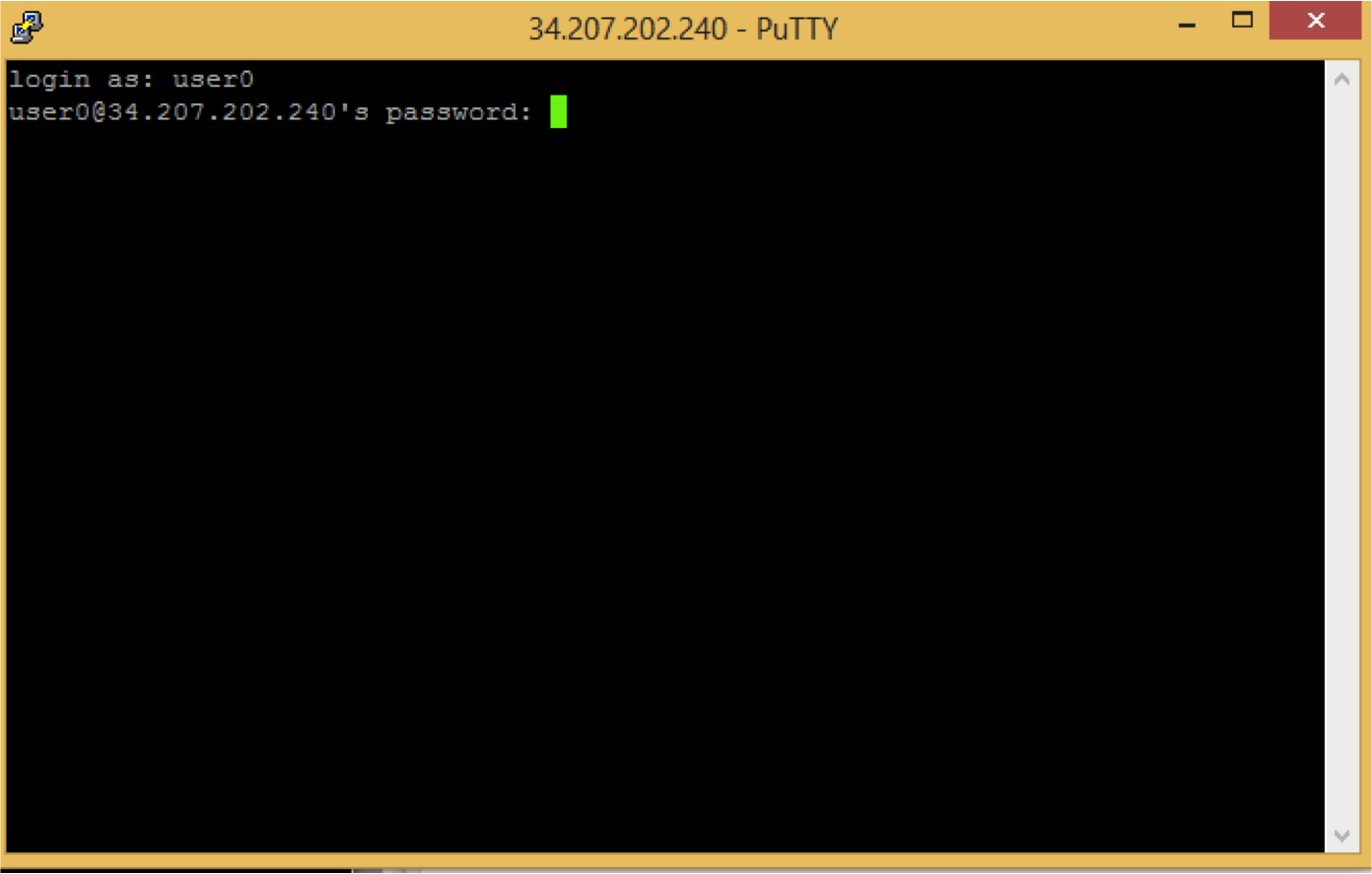
Note that linux does not show any change while typing of password.
You should see a screen like this:
For Linux/MacOSx
Open up the terminal
Run the following command to connect to the server
ssh usernameThatWillBeHandledout@34.207.202.240
You should see something like this
The introduction slides from Mostafa can be found here in in pdf format
2. Prepare your directories
## create at your home directory the following three folders
## one called Data to have the data and result you are getting from the annotation
mkdir Data
## to have the annotation database
mkdir Databases
## to have the programs we need to run.
mkdir Programs
3. Finding Open Reading Frames (ORFs)
Installation of Genemark
- Go to http://exon.gatech.edu/Genemark/license_download.cgi
- Select GeneMarkS v.4.30 and LINUX 64 and fill the form then click on the button “I agree to the terms of this license agreement”
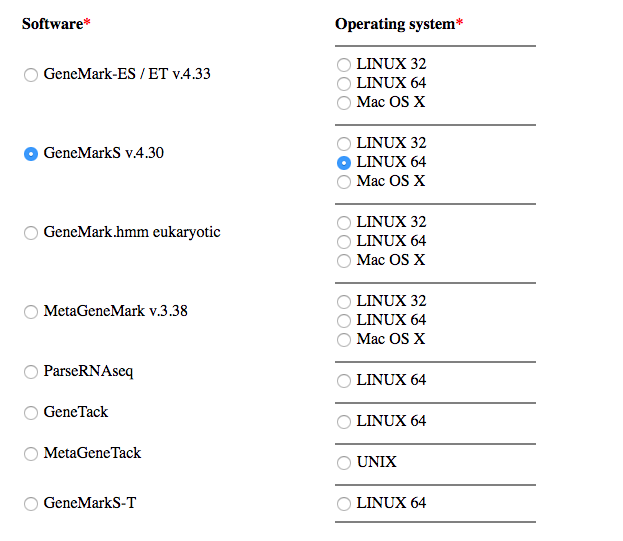
- Download both the program and the key
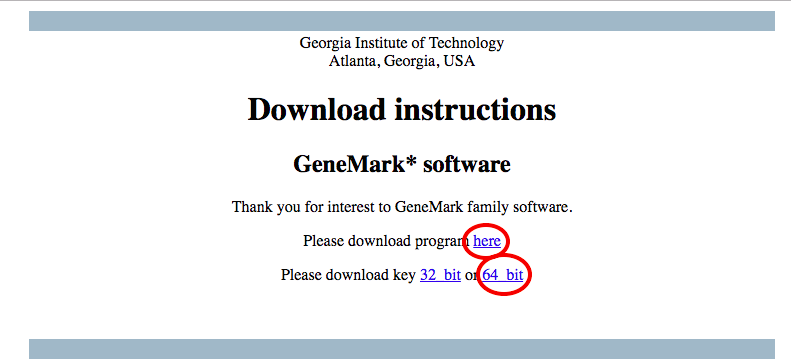
cd ~/Programs
## we need to install wget to get the data from the web.
## sudo yum install wget
## copy link address of the download program here
## and wget it
wget <the link from the website after accepting the license > ##http://topaz.gatech.edu/GeneMark/tmp/GMtool_guX8y/genemark_suite_linux_64.tar.gz
## copy link address of the key using 64_bit version
wget <the link from the website after accepting the license > ##http://topaz.gatech.edu/GeneMark/tmp/GMtool_guX8y/gm_key_64.gz
## extract both the program and the key.
tar -xvf genemark_suite_linux_64.tar.gz
gzip -d gm_key_64.gz
## copy genmarks key to the home directory
cp gm_key_64 ~/.gm_key
##
cd genemark_suite_linux_64/gmsuite
ls
Running genemark
## to see options available just write this
cd ~/Data
## we need git to get the data from the workshop
# sudo yum install git
## get the data from the workshop
git clone https://github.com/EvdH0/ASMworkshop
cp ASMworkshop/data/sample.fasta .
~/Programs/genemark_suite_linux_64/gmsuite/gmhmmp -m ~/Programs/genemark_suite_linux_64/gmsuite/MetaGeneMark_v1.mod \
-A orfs.protein.fa -D orfs.nucleotide.fa -o all.orfs.result sample.fasta
## to keep the insert information to be in the blast output.
sed -i 's/\t>/__/g' orfs.nucleotide.fa orfs.protein.fa
cat orfs.nucleotide.fa
cat orfs.protein.fa
## barcodeing the genes for both protein and nucleotide.
## coding genes
## to know how many orfs are there
grep ">" orfs.protein.fa | wc -l
## or
grep ">" orfs.nucleotide.fa | wc -l
4. Install BLAST and HMMer
Install the BLAST tool
To download BLAST at your own system visit this page. We already selected the right version in the code below.
cd ~/Programs
## if wget is not available, get it using the command below
## sudo yum install wget
## download latest version of blast
wget ftp://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/blast/executables/blast+/LATEST/ncbi-blast-2.6.0+-x64-linux.tar.gz
## download md5 signature to confirm that you download the blast completely and nothing is missing
wget ftp://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/blast/executables/blast+/LATEST/ncbi-blast-2.6.0+-x64-linux.tar.gz.md5
## check the signature if it is work
md5sum --check ncbi-blast-2.6.0+-x64-linux.tar.gz.md5
## you should see "ncbi-blast-2.6.0+-linux.tar.gz: OK"
## extract data
tar -xvf ncbi-blast-2.6.0+-x64-linux.tar.gz
## check if blast work
~/Programs/ncbi-blast-2.6.0+/bin/blastn -h
## you now see a brief list with commands that can be used with blast
Install Hmmer
## installing hiddern Markov Model searcher.
cd ~/Programs
## download the the bineary version of hmmer## remove temporary files
wget http://eddylab.org/software/hmmer3/3.1b2/hmmer-3.1b2-linux-intel-x86_64.tar.gz
## To extract data from the archive
tar -xvf hmmer-3.1b2-linux-intel-x86_64.tar.gz
##make all commands executable
chmod +x hmmer-3.1b2-linux-intel-x86_64/binaries/*
~/Programs/hmmer-3.1b2-linux-intel-x86_64/binaries/hmmscan -h
5. The first database, Resfinder
Installation of Resfinder
## to download the most updated version of resfinder
rm -rf ~/Databases/Resfinder
mkdir ~/Databases/Resfinder
cd ~/Databases/Resfinder
## sudo yum install git
git clone https://bitbucket.org/genomicepidemiology/resfinder_db.git
cd resfinder_db
## make sure all files have a linux format
## todo that you need to install dos2unix
## sudo yum install dos2unix
ls *fsa | while read file; do dos2unix $file; done
## compile them all in one file.
ls *fsa | ## show all fasta file
while read file; do ## loop through them one by one.
cat $file | ## print the whole file
awk -F"\t" '{print } END {print "\n"}'; ## add newline at the end of each file
done > ../All.resfinder.fsa ## save all these files on the file ../All.resfinder.fsa.
## to get map the Antibiotic resistance gene to a gene class
ls *fsa | while read file ; do ## loop through all fasta files
f=$(echo "$file" | cut -f1 -d.); ## get the class name from the file name.
## extract gene names from the fasta file
grep ">" $file | # extract headers of the fasta files
sed 's/>//g' | awk -F"\t" -v class="$f" '{print $1"\t"class}'; done | ## pick the first to be gene name and map it to class name
awk -F"\t" 'BEGIN {print "Gene\tClass"} {print $1"\t"$2 }' > ../Resfinder.gene.class
## to check if you have the right file format
## two column
## ARGGene class
head ../Resfinder.gene.class
cd ..
mkdir blastNA
cd blastNA
~/Programs/ncbi-blast-2.6.0+/bin/makeblastdb -in ../All.resfinder.fsa -title RESFINDERNucl \
-out RESFINDERNucl -input_type fasta -hash_index -dbtype nucl
Run Resfinder
cd ~/Data
mkdir Resfinder
cd Resfinder
## nucleotide versus Resfinder nucleotide
## blast orfs against the Resfinder nucleotide blastdb
time ~/Programs/ncbi-blast-2.6.0+/bin/blastn -query ../orfs.nucleotide.fa \
-db ~/Databases/Resfinder/blastNA/RESFINDERNucl -outfmt 6 \
-max_target_seqs 1 -evalue 1E-50 -word_size 6 -num_threads 1 -out orf.resfinder.NA.versus.NA.tab
## to see the result of the blast
cat orf.resfinder.NA.versus.NA.tab
See what antibiotic resistance genes maps to
## fruther annotation
## maping gene to class
##
join -t $'\t' -1 2 -2 1 <(sort -k2 orf.resfinder.NA.versus.NA.tab ) \
<(sort ~/Databases/Resfinder/Resfinder.gene.class) > orf.resfinder.NA.versus.NA.tab.geneClass
cat orf.resfinder.NA.versus.NA.tab.geneClass
## how many gene classes are there?
## how many betalactamases are there?
## how many inserts have resistance gene?
6. CARD
Install the CARD database
# getting and installing
cd ~/Databases
mkdir CARD
cd CARD
mkdir RawData
cd RawData
wget https://card.mcmaster.ca/download/0/broadstreet-v1.1.8.tar.gz
ls
## maybe
##sudo yum install bzip2
tar -xvf broadstreet-v1.1.8.tar.gz
ls
## to show the card nucleotide fasta files
ls nucleotide_fasta_*
cat nucleotide_fasta_* > ../All.CARD.NA.fa
ls protein_fasta_*
cat protein_fasta_* > ../All.CARD.AA.fa
Compile CARD Databases
## to insure that you are at the right place.
cd ~/Databases/CARD/
mkdir blastNA blastAA
## compiling blast protein database for CARD
cd blastAA
~/Programs/ncbi-blast-2.6.0+/bin/makeblastdb -in ../All.CARD.AA.fa -title CARDProt \
-out CARDProt -input_type fasta -hash_index -dbtype prot
## to confirm that you are at ~/Databases/CARD/
cd ..
## compiling blast Nucleotides database for CARD
cd blastNA
~/Programs/ncbi-blast-2.6.0+/bin/makeblastdb -in ../All.CARD.NA.fa -title CARDNucl \
-out CARDNucl -input_type fasta -hash_index -dbtype nucl
Run the CARD database
## Run CARD databses
cd ~/Data
mkdir CARD
cd CARD
## nucleotide versus card nucleotide
~/Programs/ncbi-blast-2.6.0+/bin/blastn -query ../orfs.nucleotide.fa -db ~/Databases/CARD/blastNA/CARDNucl -outfmt 6 \
-max_target_seqs 10 -evalue 1E-50 -word_size 6 -num_threads 1 -out orf.card.NA.versus.NA.tab
## to get the top hit based on bitscore.
sort -k1,1 -k12,12nr orf.card.NA.versus.NA.tab |
awk -F"\t" '{if(FNR==1) {geneID=$1; print $0} else
{if(geneID!=$1) {geneID=$1; print $0}}}' > orf.card.NA.versus.NA.tab.top1.txt
wc -l orf.card.NA.versus.NA.tab.top1.txt
## to show the frequency of Antibiotic resistance genes observed.
cut -f1,2 orf.card.NA.versus.NA.tab.top1.txt | sort -u | cut -f2 | sort |
uniq -c |
awk '
BEGIN {print "Gene\tNumberOfORFsObserved"; sum=0;}
{print $2"\t"$1; sum=sum+$1}
END {print "Total\t"sum}'
## protein versus card protein
~/Programs/ncbi-blast-2.6.0+/bin/blastp -query ../orfs.protein.fa -db ~/Databases/CARD/blastAA/CARDProt -outfmt 6 \
-max_target_seqs 10 -evalue 100 -word_size 4 -num_threads 1 -out orf.card.AA.versus.AA.tab
sort -k1,1 -k12,12nr orf.card.AA.versus.AA.tab |
awk -F"\t" '{if(FNR==1) {geneID=$1; print $0} else
{if(geneID!=$1) {geneID=$1; print $0}}}' > orf.card.AA.versus.AA.tab.top1.txt
## to show the number of Antibiotic resistance genes observed.
wc -l orf.card.AA.versus.AA.tab.top1.txt
## to show the frequency of Antibiotic resistance genes observed.
cut -f1,2 orf.card.AA.versus.AA.tab.top1.txt | sort -u | cut -f2 | sort |
uniq -c |
awk '
BEGIN {print "Gene\tNumberOfORFsObserved"; sum=0;}
{print $2"\t"$1; sum=sum+$1}
END {print "Total\t"sum}'
7. Protein domains using PFAM
Install and running PFAM
## get the PFAM necessary files
## compile databases
## query databases
## list domains
## Download the pfam from the ftp servcer ftp://ftp.ebi.ac.uk/pub/databases/Pfam/releases/ choose the most recent one.
## for now we are using Pfam31
mkdir ~/Databases/PFAM
cd ~/Databases/PFAM
## download pfam hmm database
wget ftp://ftp.ebi.ac.uk/pub/databases/Pfam/releases/Pfam31.0/Pfam-A.hmm.gz
## get
time gzip -d Pfam-A.hmm.gz
## compile database
time ~/Programs/hmmer-3.1b2-linux-intel-x86_64/binaries/hmmpress Pfam-A.hmm
mkdir ~/Data/PFAM
cd ~/Data/PFAM
## identify pfam domains of the orfs
## needed protein sequences of the orfs
time ~/Programs/hmmer-3.1b2-linux-intel-x86_64/binaries/hmmscan --cpu 1 --notextw --noali --tblout \
PFAM.result ~/Databases/PFAM/Pfam-A.hmm ../orfs.protein.fa
cat PFAM.result